Quick Start
This guide will cover:
- Use Kind create three kubernetes cluster
- Install
kosmoscontrol plane components in a Kubernetes cluster which is known ashost cluster. - Join a member cluster to
kosmoscontrol plane on thehost cluster. - Enabling cross-cluster deployment of applications through Kosmos.
Prerequisites
Deploy and run Kosmos use script
run the following script:
git clone https://github.com/kosmos-io/kosmos.git && cd kosmos
hack/local-up-kosmos.sh
Deploy and run Kosmos use kosmosctl
1. Use Kind create cluster
- Config your kind cluster use flow config, change the param as you need
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
networking:
# WARNING: It is _strongly_ recommended that you keep this the default
# (127.0.0.1) for security reasons. However it is possible to change this.
apiServerAddress: "192.168.200.112"
# By default the API server listens on a random open port.
# You may choose a specific port but probably don't need to in most cases.
# Using a random port makes it easier to spin up multiple clusters.
apiServerPort: 1443
nodes:
- role: control-plane
extraPortMappings:
- containerPort: "{{container_port}}"
hostPort: "{{host_port}}"
protocol: TCP
listenAddress: "{{host_ipaddress}}"
#- role: worker
#- role: worker
-
create cluster1
kind create cluster -n kind-cluster1 --config /path/to/kind-config -
create cluster2
kind create cluster -n kind-cluster2 --config /path/to/kind-config -
create cluster3
kind create cluster -n kind-cluster3 --config /path/to/kind-config
2. Install kosmosctl client
Kosmos is equipped with a tool called kosmosctl, which allows for quick deployment of Kosmos components, adding clusters, and testing network connectivity.Install kosmosctl, you can download from the releases page or build from source
2.1 Method 1:Use prebuild Binary executable file
- Download from the releases page, only support macOS and linux
- put
kosmosctlto you Path, so you can executekosmosctlwithout absolute path - recommend use linux to install kosmosctl
wget -cO kosmosctl-linux-amd64 https://github.com/kosmos-io/kosmos/releases/download/v0.2.0-lts/kosmosctl-linux-amd64
chmod +x kosmosctl-linux-amd64 && sudo install -m 755 kosmosctl-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/kosmosctl
2.2 Method 2:Build from source
- Download source
git clone https://github.com/kosmos-io/kosmos.git - Build code, the output file is in the
<project_dir>/_output/bin/linux/amd64/kosmosctlmake kosmosctl VERSION=v0.1.9] - you can find any available version or tags in here
3. Install kosmos control plane components
- Install the control plane in the
host cluster. Please config the pod can access the kind cluster apiServer, avoid thekosmos-operatorCrashLoopBackOff
kosmosctl install --cni calico --default-nic eth0 //We build a network tunnel based the network interface value passed by the arg default-nic
4. Cluster management
- Get the cluster2 and cluster3 kubeconfig and put it on the
host cluster,join the two member clusters(execute on the host cluster).
kosmosctl join cluster --name cluster2 --kubeconfig ~/kubeconfig/cluster1-kubeconfig --cni calico --default-nic eth0 --enable-all
kosmosctl join cluster --name cluster3 --kubeconfig ~/kubeconfig/cluster2-kubeconfig --cni calico --default-nic eth0 --enable-all
5. Check the cluster management status(Use the Kosmos clusters like single cluster on the control plane)
- check cluster nodes status
kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
kosmos-cluster1-control-plane Ready control-plane 9d v1.27.3
kosmos-cluster2 Ready agent 9d v1.27.3
kosmos-cluster3 Ready agent 9d v1.27.3
- check cluster status
kubectl get clusters
NAME NETWORK_TYPE IP_FAMILY
cluster2 gateway ipv4
cluster3 gateway ipv4
kosmos-control-cluster gateway ipv4
Deploy and run Kosmos use Helm
1. Use Kind create cluster
- Config your kind cluster use flow config, change the param as you need
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
networking:
# WARNING: It is _strongly_ recommended that you keep this the default
# (127.0.0.1) for security reasons. However it is possible to change this.
apiServerAddress: "192.168.200.112"
# By default the API server listens on a random open port.
# You may choose a specific port but probably don't need to in most cases.
# Using a random port makes it easier to spin up multiple clusters.
apiServerPort: 1443
nodes:
- role: control-plane
extraPortMappings:
- containerPort: "{{container_port}}"
hostPort: "{{host_port}}"
protocol: TCP
listenAddress: "{{host_ipaddress}}"
#- role: worker
#- role: worker
-
create cluster1
kind create cluster -n kind-cluster1 --config /path/to/kind-config -
create cluster2
kind create cluster -n kind-cluster2 --config /path/to/kind-config -
create cluster3
kind create cluster -n kind-cluster3 --config /path/to/kind-config
2. Download the Helm deployment file for Kosmos
-
Download the source code for Kosmos
git clone https://github.com/kosmos-io/kosmos.git -
Place the
kosmosfolder from thechartsmodule of the source code into thehost cluster.
3. Install Kosmos control plane components
- Install the control plane in the
host cluster. Please config the pod can access the kind cluster apiServer, avoid thekosmos-operatorCrashLoopBackOff,modify the configuration values in thevalue.yamlfile within the downloadedkosmosfolder (especially the ns, kubeconfig information in the main cluster, images, etc.) to meet the requirements of the current environment. For specific configuration details, refer to the comments.
kubectl create ns kosmos-system
helm install kosmos -n kosmos-system kosmos
4. Check the installation status of the Kosmos control plane components
kubectl get all -n kosmos-system
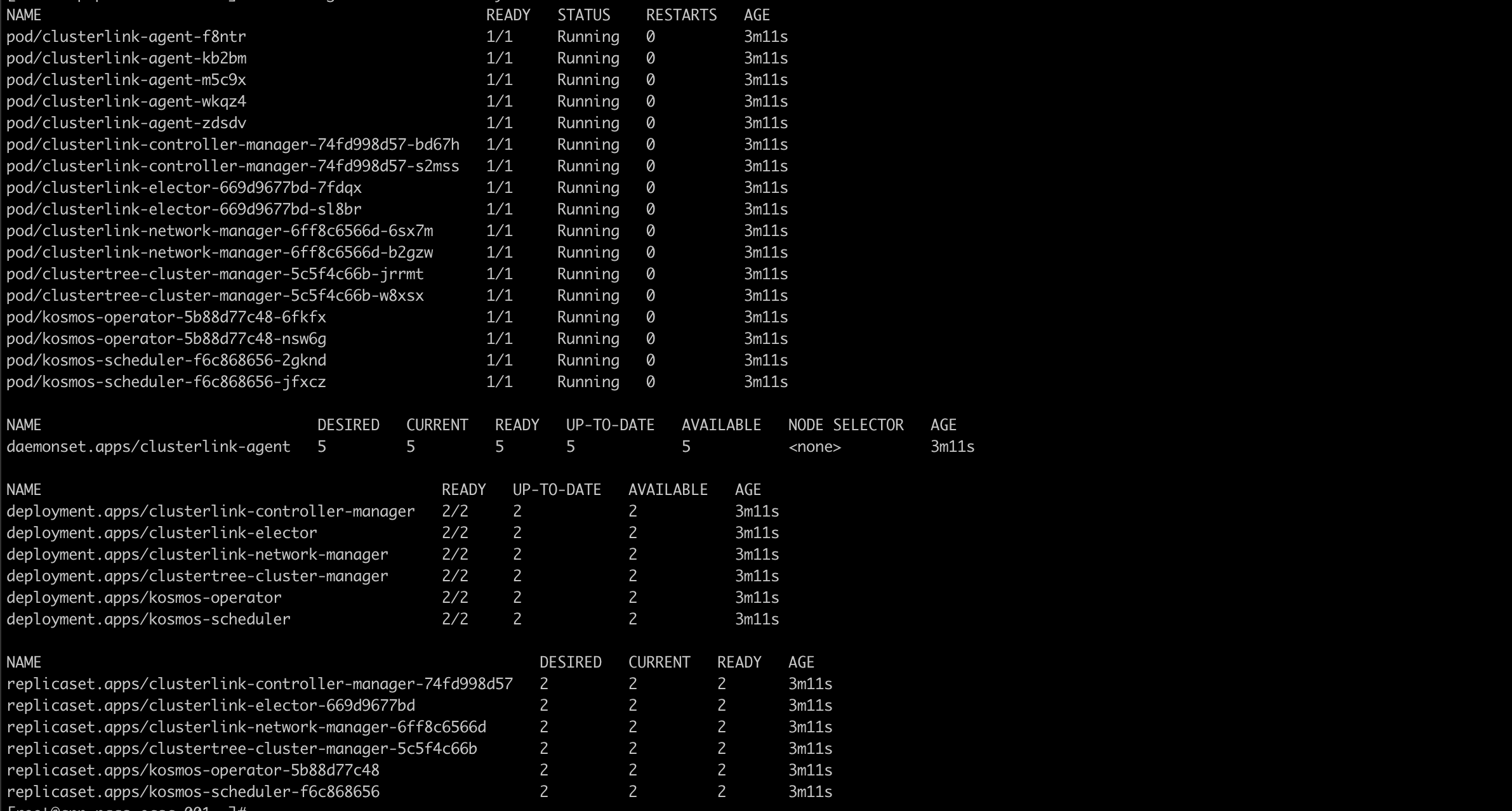
5. Cluster management
All cluster management operations by Kosmos are conducted within the host cluster, and both the host and member clusters need to be managed. Managing the host cluster facilitates subsequent management operations for the member clusters, as well as the inter-cluster container network integration. Place the cluster_yaml folder from the deploy module in the source code into the host cluster.
- Manage the
host cluster
Modify the commented content in the kosmos-control-cluster.yaml file within cluster_yaml.
kubectl apply -f kosmos-control-cluster.yaml
After successfully managing the host cluster, check if the cluster object for the host cluster has been created. You can see detailed information in the cluster object, particularly noting that the status section includes new clusterLinkStatus information, which encompasses podCIDRS and serviceCIDRS.
kubectl get cluster kosmos-control-cluster -oyaml
- Manage the
member cluster
Modify the contents of the comments in member-cluster.yaml (if there are multiple member clusters, multiple files are needed) to make them fully consistent with the information in the managed subordinate clusters (including node network interface card information, etc.).
kubectl apply -f member-cluster.yaml
After successfully managing the member cluster, check whether the cluster object in the member cluster has been created. You can see detailed information in the cluster object, particularly the newly added clusterLinkStatus information in the status section, which includes podCIDRS and serviceCIDRS.
kubectl get cluster member-cluster -oyaml
Verify in the host cluster whether the member clusters are successfully managed as virtual nodes.
kubectl get nodes
Kosmos supports one-to-one cluster-level management and can also manage all or some nodes within a single cluster. The mode can be modified in the cluster object.
6. Check after successful Kosmos cluster management
host clusterinspection
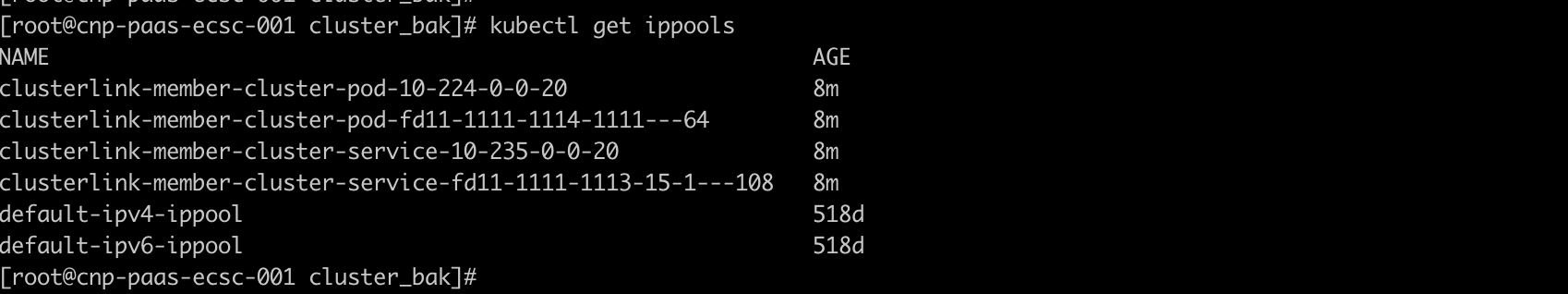
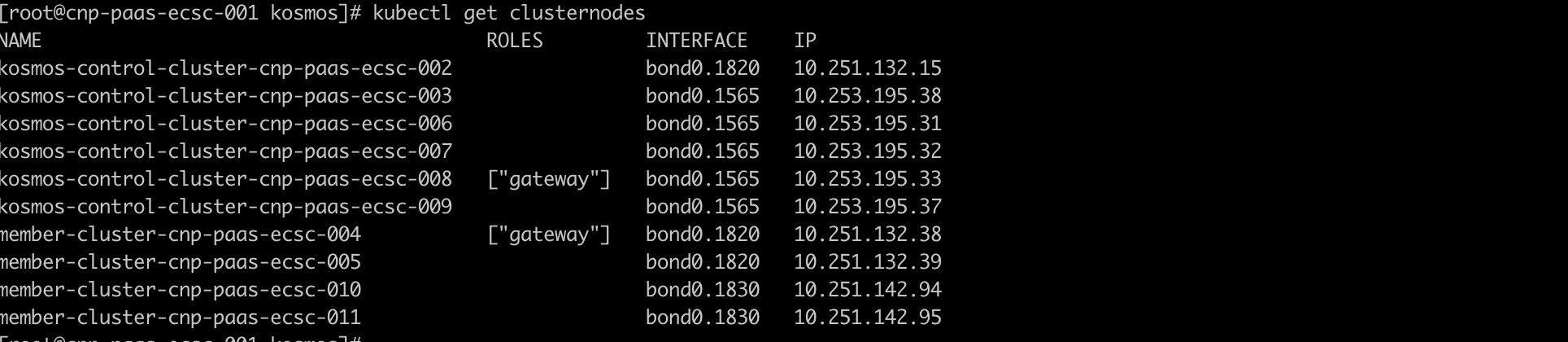
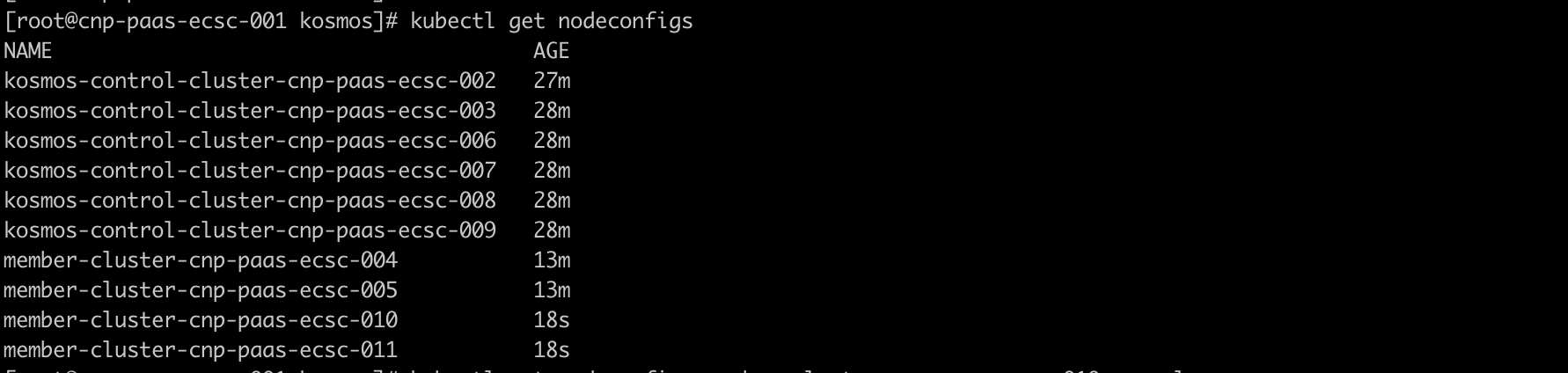
When cross-cluster container network issues arise, whether in p2p mode or gateway mode, network troubleshooting (such as packet capturing) can be carried out on the network interfaces prefixed with vx created by Kosmos.
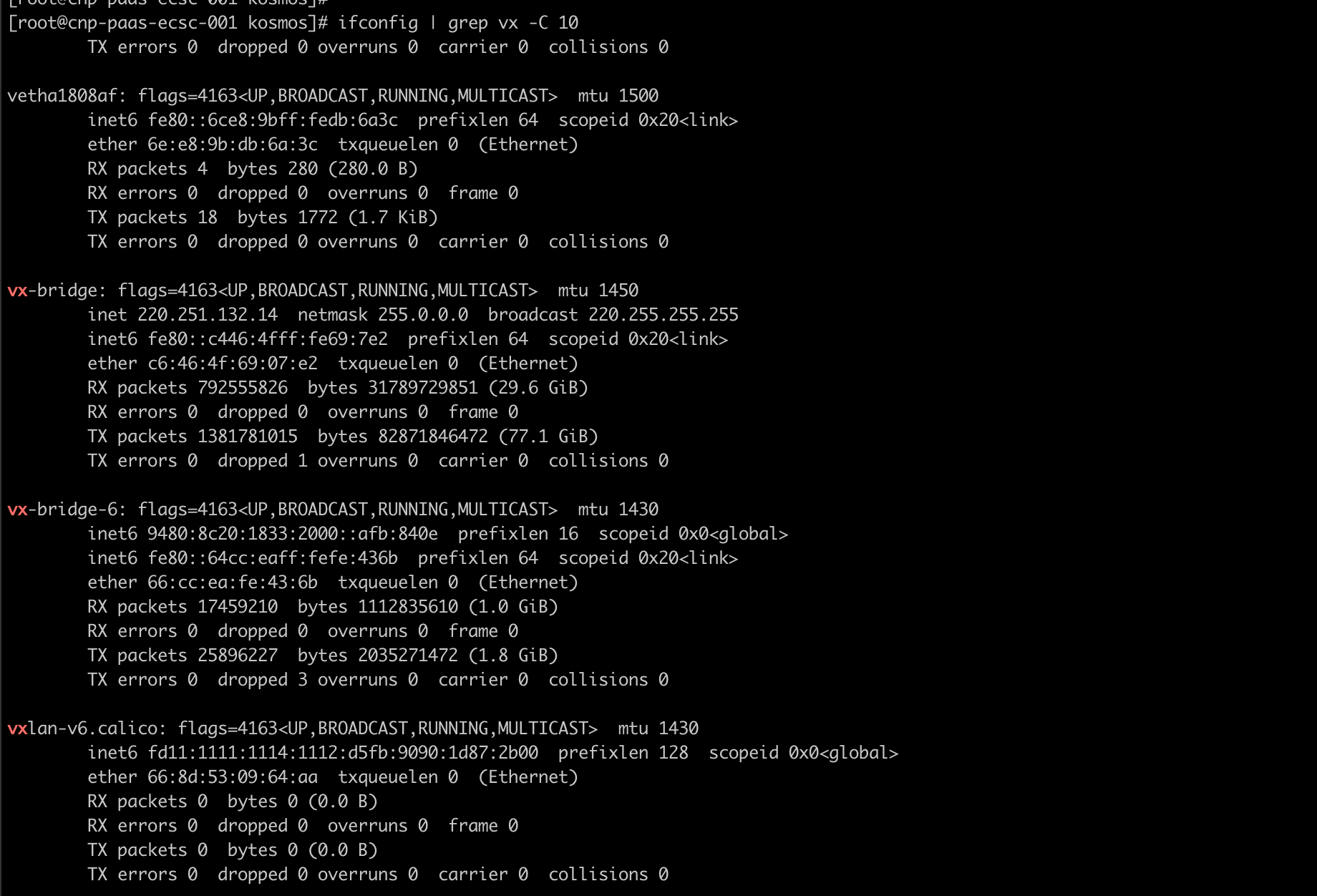
member clusterinspection
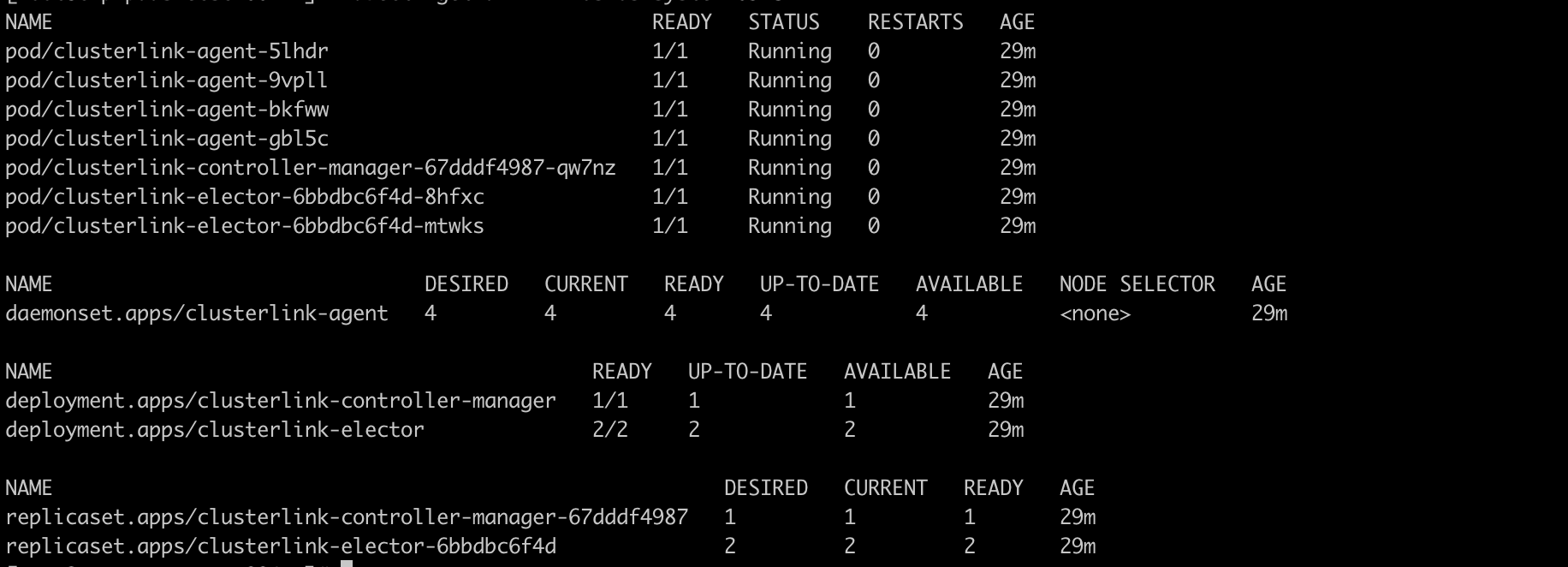
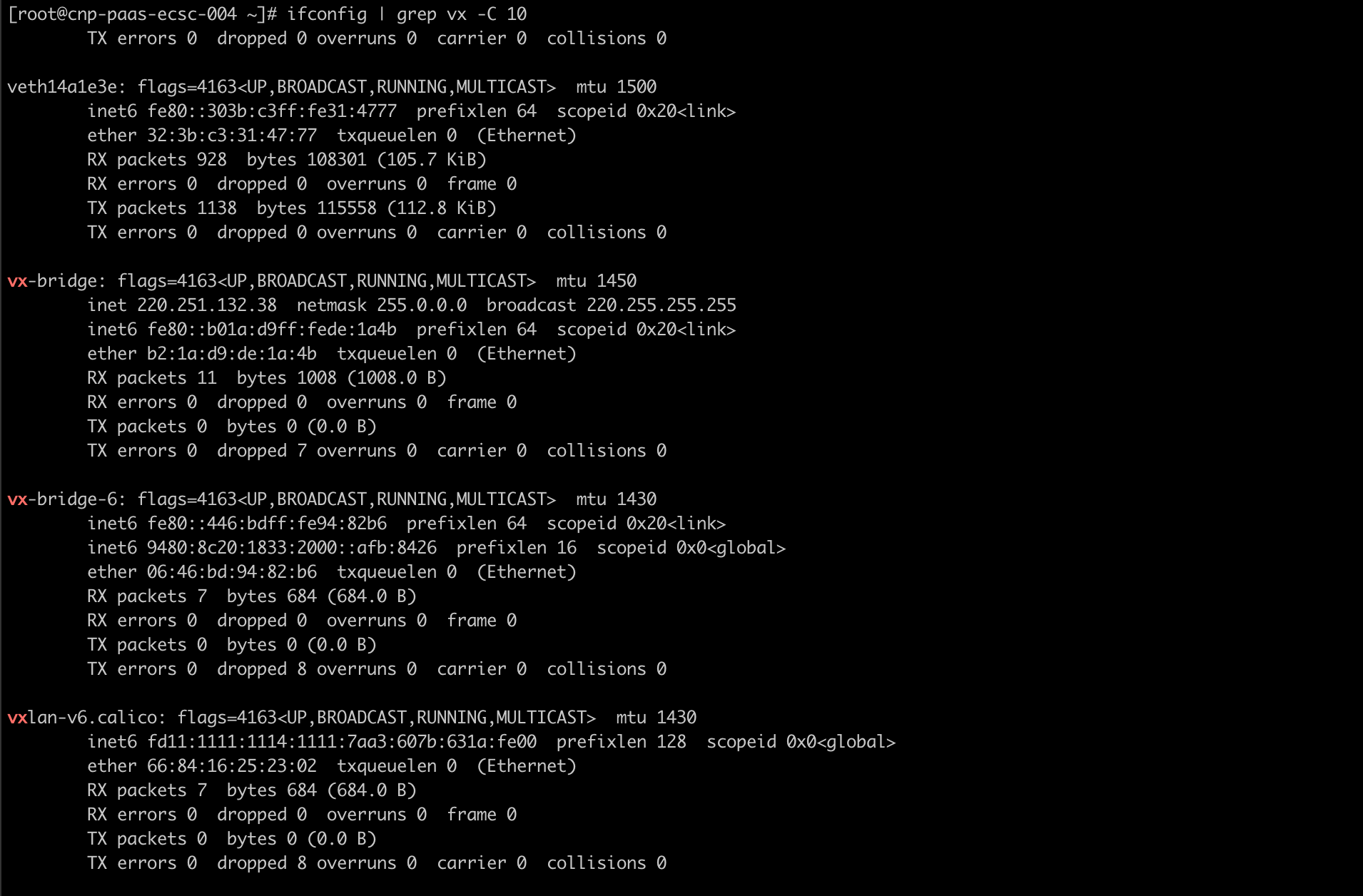
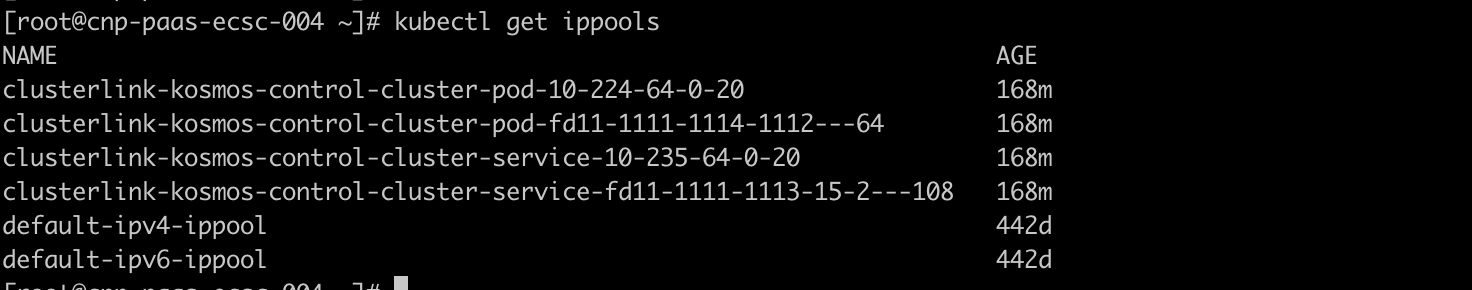
Deploy nginx use kosmos
Edit the Nginx service YAML
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
tolerations:
- key: kosmos.io/node
operator: Equal
value: "true"
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80
Execute Nginx service YAML
kubectl apply -f nginx-deploy.yml
Check the status of Nginx service Pods
kubectl get pods -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx-deployment-887b5c6bb-jx9kq 1/1 Running 0 18h 10.244.0.8 kosmos-cluster3 <none> <none>
nginx-deployment-887b5c6bb-kc9ff 1/1 Running 0 41h 10.244.0.7 kosmos-cluster2 <none> <none>
nginx-deployment-887b5c6bb-vz8vk 1/1 Running 0 41h 10.244.0.7 kosmos-cluster3 <none> <none>
To summarize, the cross-cluster deployment of the Nginx service based on Kosmos has been completed, with the service running in the member clusters