Multi-cluster Scheduler
After Kosmos join a member cluster, it will map a virtual node with the kosmos.io/node=true:Noschedule taint, so the Kubernetes default scheduler cannot schedule Pods to the virtual node (i.e, the member cluster).
After deploying the kosmos-scheduler, users can tolerate the kosmos.io/node=true:Noschedule taint through the LeafNodeTaintToleration scheduling plugin in kosmos-scheduler to achieve an indiscriminate mixed scheduling effect between member cluster and host cluster nodes.
For Pods with PV/PVC, you also need to configure the LeafNodeVolumeBinding scheduling plugin in kosmos-scheduler to directly use the virtual node with the kosmos.io/node=true:Noschedule taint during the storage volume binding process.
It should be noted that for different versions of Kubernetes, the scheduling module (Scheduler Framework) on which the published default scheduler depends will also change with the version. Currently, Kosmos has also adapted to the two versions (release-1.21.5 and release-1.26.3).
The following verification part will be deployed and tested with release-1.21.5.
Multi-cluster Scheduler Solution
Introduction
The Scheduler framework was first introduced through the 624-scheduling-framework proposal of kubernetes enhancements, mainly to achieve the following goals:
- Make scheduler more extendable.
- Make scheduler core simpler by moving some of its features to plugins.
- Propose extension points in the framework.
- Propose a mechanism to receive plugin results and continue or abort based on the received results.
- Propose a mechanism to handle errors and communicate them with plugins.
For this purpose, the scheduler framework defines multiple extension points as follows:
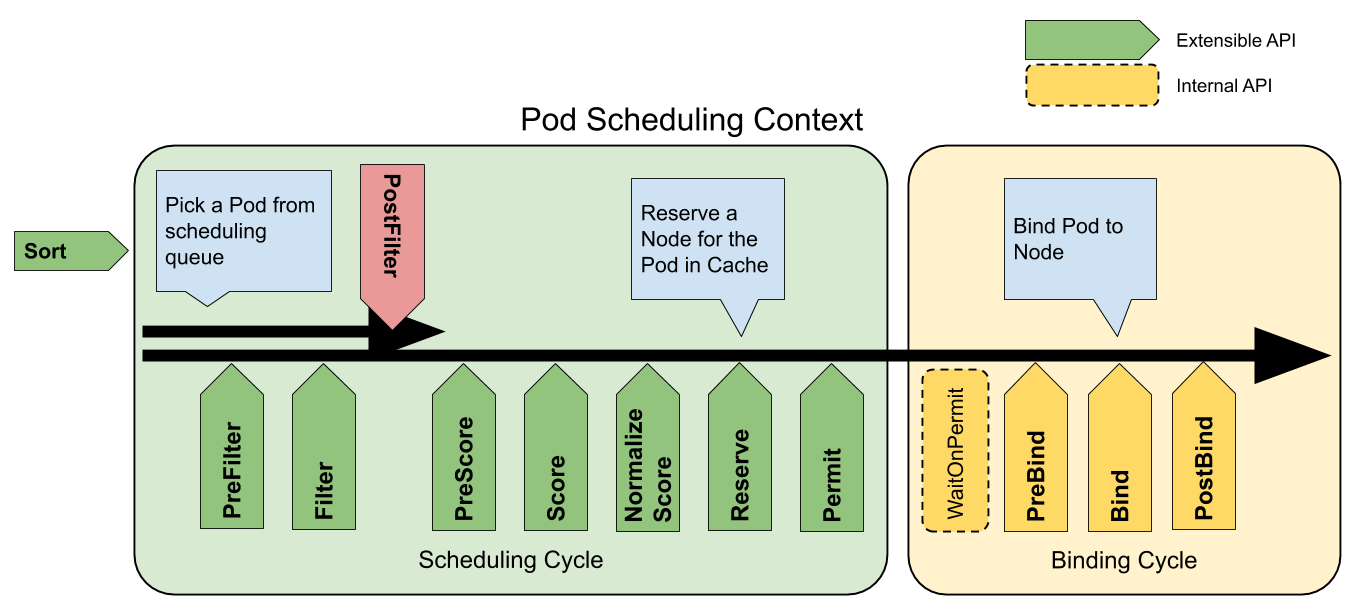
LeafNodeTaintToleration and LeafNodeVolumeBinding scheduling plugins in kosmos-scheduler are mainly optimized based on the NodeTaintToleration and NodeVolumeBinding scheduling plugins of the Kubernetes default scheduler.
LeafNodeTaintToleration plugin mainly adds tolerance to the kosmos.io/node=true:Noschedule taint in the virtual node in the Filter extension point.
LeafNodeVolumeBinding plugin mainly acts on the Filter, Reserve, Unreserved, and PreBind extension points, and directly passes the virtual node with the kosmos.io/node=true:Noschedule taint.
Prerequisites
Install Kosmos
Refer to the Kosmos Quick Start documentation https://github.com/kosmos-io/kosmos and enable the ClusterLink module for multi-cluster networking. Using the kosmosctl tool:
kosmosctl install --cni calico --default-nic eth0 (We build a network tunnel based on the network interface value passed by the arg default-nic)
At least the clustertree module is deployed and join the leaf cluster correctly.
Join the Leaf Cluster
kosmosctl join cluster --name cluster1 --kubeconfig ~/kubeconfig/cluster1-kubeconfig --cni calico --default-nic eth0 --enable-link
Deploy Kosmos-scheduler
- Configure scheduler and scheduling policy:
---
# kosmos-scheduler scheduling policy
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: scheduler-config
namespace: kosmos-system
data:
scheduler-config.yaml: |
apiVersion: kubescheduler.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: KubeSchedulerConfiguration
leaderElection:
leaderElect: true
resourceName: kosmos-scheduler
resourceNamespace: kosmos-system
profiles:
- schedulerName: kosmos-scheduler
plugins:
preFilter:
disabled:
- name: "VolumeBinding"
enabled:
- name: "LeafNodeVolumeBinding"
filter:
disabled:
- name: "VolumeBinding"
- name: "TaintToleration"
enabled:
- name: "LeafNodeTaintToleration"
- name: "LeafNodeVolumeBinding"
score:
disabled:
- name: "VolumeBinding"
reserve:
disabled:
- name: "VolumeBinding"
enabled:
- name: "LeafNodeVolumeBinding"
preBind:
disabled:
- name: "VolumeBinding"
enabled:
- name: "LeafNodeVolumeBinding"
pluginConfig:
- name: LeafNodeVolumeBinding
args:
bindTimeoutSeconds: 5
---
# scheduler config
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: kosmos-scheduler
namespace: kosmos-system
labels:
component: scheduler
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
component: scheduler
template:
metadata:
labels:
component: scheduler
spec:
volumes:
- name: scheduler-config
configMap:
name: scheduler-config
defaultMode: 420
containers:
- name: kosmos-scheduler
image: ghcr.io/kosmos-io/scheduler:0.0.2
command:
- scheduler
- --config=/etc/kubernetes/kube-scheduler/scheduler-config.yaml
resources:
requests:
cpu: 200m
volumeMounts:
- name: scheduler-config
readOnly: true
mountPath: /etc/kubernetes/kube-scheduler
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 10259
scheme: HTTPS
initialDelaySeconds: 15
periodSeconds: 10
failureThreshold: 3
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 10259
scheme: HTTPS
restartPolicy: Always
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
serviceAccountName: kosmos-scheduler
serviceAccount: kosmos-scheduler
- Verify the kosmos-scheduler service:
# kosmos-scheduler is created.
kubectl -n kosmos-system get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kosmos-scheduler-8f96d87d7-ssxrx 1/1 Running 0 24s
Try a Sample
-
Deploy openebs on the test cluster
-
Use case yaml(mysql-cluster.yaml)
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
namespace: test-mysql
name: my-secret
type: Opaque
data:
# root password is required to be specified
ROOT_PASSWORD: ${your_password}
## application credentials that will be created at cluster bootstrap
# DATABASE:
# USER:
# PASSWORD:
---
kind: MysqlCluster
metadata:
name: test-mysql-cluster
namespace: test-mysql
spec:
replicas: 2
secretName: my-secret
image: docker.io/percona:5.7
mysqlVersion: "5.7"
podSpec:
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchLabels:
mysql.presslabs.org/cluster: test-mysql-cluster
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
volumeSpec:
persistentVolumeClaim:
storageClassName: openebs-hostpath
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
- Operation instructions
# List all nodes in the host cluster
kubectl get node
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
kosmoscluster1-1 Ready control-plane,master,node 21d v1.21.5-eki.0
kosmoscluster1-2 Ready node 21d v1.21.5-eki.0
kosmos-member2-cluster-1 Ready agent 24m v1.21.5-eki.0
kosmos-member2-cluster-2 Ready agent 24m v1.21.5-eki.0
# Show the taint information on the virtual node
kubectl describe node kosmos-member2-cluster-1 |grep Tai
Taints: node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute
kubectl describe node kosmos-member2-cluster-2 |grep Tai
Taints: node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute
# Scheduling by the kosmos-scheduler (hybrid scheduling)
kubectl apply -f mysql-cluster.yaml
# Show instances (hybrid) scheduling result in host cluster
kubectl get pod -owide -n test-mysql
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
test-mysql-cluster-mysql-0 4/4 Running 0 3m 2409:xxxxx:8ac kosmoscluster1-2 <none> <none>
test-mysql-cluster-mysql-1 4/4 Running 0 2m 2409:xxxxx:8ae kosmos-member2-cluster-1 <none> <none>
# Show instances (hybrid) scheduling result in member cluster
kubectl get pod -owide -n test-mysql
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
test-mysql-cluster-mysql-1 4/4 Running 0 2m 2409:xxxxx:8ae kosmos-member2-cluster-1 <none> <none>
Conclusion
You can see that kosmos-scheduler successfully schedules the Pods of the user instances to the host cluster and member clusters.