Kosmos Node NotReady
Kosmos Node NotReady Solution
Introduction
Assuming that we have registered the cluster cluster7 on the master cluster:
$ kubectl get node
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
ecs-54004033-001 Ready worker 50d v1.21.5
ecs-54004033-002 Ready control-plane,master,worker 50d v1.21.5
kosmos-cluster7 Ready agent 5d22h v1.21.5
The clustertree-cluster-manager of Kosmos will continuously monitor the resource usage and cluster status of the cluster7 cluster, and update it to the leaf node kosmos-cluster7 on the master cluster.
$ kubectl get deploy -nkosmos-system
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
clusterlink-controller-manager 1/1 1 1 5d22h
clusterlink-elector 2/2 2 2 5d22h
clusterlink-network-manager 1/1 1 1 5d22h
clustertree-cluster-manager 1/1 1 1 5d22h
kosmos-operator 1/1 1 1 5d22h
kosmos-webhook 1/1 1 1 11
If there is a network fluctuation between the master cluster and the cluster7 cluster, Kosmos will detect this anomaly and set the status of the leaf node kosmos-cluster7 on the master cluster to "not ready". This will trigger the pod eviction behavior in Kubernetes, meaning that the pods on the "not ready" node will be evicted to other ready nodes.
However, due to network fluctuations, the status of kosmos-cluster7 may become "ready" again during the eviction process. But the events of the originally evicted pods will still be sent to the "cluster7" cluster, causing normal running pods on the "cluster7" cluster to be deleted or restarted, thus affecting the business.
Solution: Integrating Kyverno to solve the kosmos node is not ready
Kyverno validate, mutate, generate, and cleanup configurations using Kubernetes admission webhook, background scans, and source code repository scans. Kyverno policies can be managed as Kubernetes resources.
Its main functions are as follows:
- validate, mutate, generate, or cleanup (remove) any resource
- verify container images for software supply chain security
- match resources using label selectors and wildcards
- synchronize configurations across Namespaces
- block non-conformant resources using admission controls, or report policy violations
This article explains how to use Kyverno's admission webhook to prevent pod expulsion when the kosmos node is not ready.
What is an admission webhook?
An "admission webhook" is a piece of code that intercepts requests to the Kubernetes API Server before object persistence. It allows requests to pass through after authentication and authorization. Admission controllers can perform validation, mutation, or both. Mutating controllers modify the resource objects they handle, while Validating controllers do not. If any controller in any phase rejects a request, the entire request will be immediately rejected, and the error will be returned to the end user.
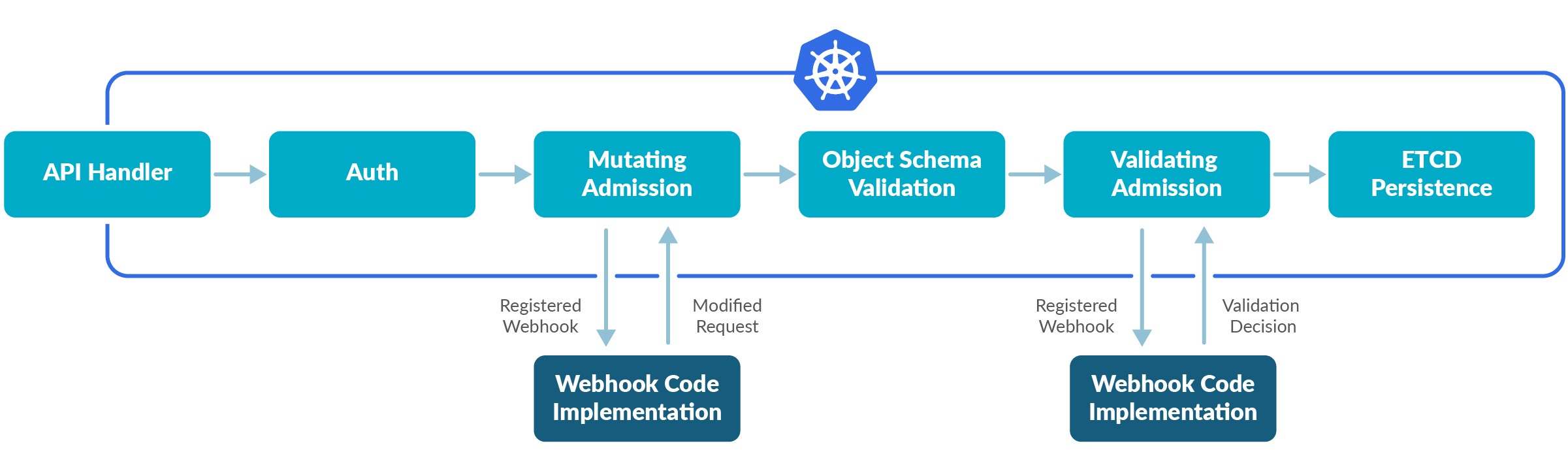
Solution
install Kyverno
kubectl create -f https://github.com/kyverno/kyverno/releases/download/v1.10.0/install.yaml
Configuring clusterpolicy
There are four scenarios in which k8s evicts the pod:
- User initiated : The user initiates the evict request initiated by the API. For example, all Pods on the node are evicted during node maintenance to avoid the impact on services caused by the node going offline suddenly.
- Kubelet initiated : Periodically checks the resources of the node. When the resources are insufficient, some Pods are evicted based on the priority.
- kube-controller-manager Initiate : Periodically detects all nodes. When a node is in the NotReady state for more than a period of time, all Pods on the node are evicted so that they are scheduled to other normal nodes for re-running. When taint evict is enabled, the pod that cannot tolerate the taint is exicted immediately after there is a 'NoExecute' taint on node. For the pod that can tolerate the taint, the pod will be evicted after the minimum taint tolerance time configured on the pod.
- kube-scheduler Initiating : When preemptive scheduling is implemented, the low-priority Pod may be evicted to make room for the high-priority & preemptive Pod, so that the high-priority Pod can be scheduled normally
With the following profile, we will only block pod deletion events that meet the following three conditions:
(1) Node status is NotReady
(2) Node is a KosmosNode
(3) the Username is system: serviceaccount: kube-system:node-controller (belong to kube-controller-manager of node-controller )
apiVersion: kyverno.io/v1
kind: ClusterPolicy
metadata:
name: kosmos-node-not-ready
spec:
validationFailureAction: Enforce
background: false
rules:
- match:
any:
- resources:
kinds:
- Pod
operations:
- DELETE
name: kosmos-node-not-read
context:
- name: nodeStatus
apiCall:
urlPath: /api/v1/nodes/{{request.oldObject.spec.nodeName}}
jmesPath: status.conditions[?type=='Ready'].status | [0]
- name: isKosmosNode
apiCall:
urlPath: /api/v1/nodes/{{request.oldObject.spec.nodeName}}
jmesPath: metadata.labels."kosmos.io/node"
preconditions:
all:
- key: "{{ request.userInfo.username }}"
operator: Equals
value: "system:serviceaccount:kube-system:node-controller"
- key: "{{ nodeStatus }}"
operator: NotEquals
value: "True"
- key: "{{ length(isKosmosNode) }}"
operator: GreaterThan
value: 0
validate:
message: " {{ request.userInfo.username }} delete pod {{request.oldObject.metadata.name}} of NotReady Kosmos {{request.oldObject.spec.nodeName}} Node is not allowed. "
deny: {}
When the status of Kosmos node is notready, the Pods on this node are blocked. You can view the following logs by viewing the kyverno-admission-controller
handlers.go:139] webhooks/resource/validate "msg"="admission request denied" "clusterroles"=["system:basic-user","system:controller:node-controller","system:discovery","system:public-info-viewer","system:service-account-issuer-discovery"] "gvk"={"group":"","version":"v1","kind":"Pod"} "gvr"={"group":"","version":"v1","resource":"pods"} "kind"="Pod" "name"="example-deployment-6cc4fd9bd7-kkm8z" "namespace"="default" "operation"="DELETE" "resource.gvk"={"Group":"","Version":"v1","Kind":"Pod"} "roles"=null "uid"="7f25ee88-4522-45fd-a6ba-38733122b443" "user"={"username":"system:serviceaccount:kube-system:node-controller","uid":"5a13be66-71fd-40e3-9553-00eb0825fbb0","groups":["system:serviceaccounts","system:serviceaccounts:kube-system","system:authenticated"]}
event.go:307] "Event occurred" object="kosmos-node-not-ready" fieldPath="" kind="ClusterPolicy" apiVersion="kyverno.io/v1" type="Warning" reason="PolicyViolation" message="Pod default/example-deployment-6cc4fd9bd7-kkm8z: [kosmos-node-not-ready] fail (blocked); system:serviceaccount:kube-system:node-controller delete pod example-deployment-6cc4fd9bd7-kkm8z of NotReady Kosmos kosmos-cluster2 Node is not allowed. "
validation.go:103] webhooks/resource/validate "msg"="validation failed" "action"="Enforce" "clusterroles"=["system:basic-user","system:controller:node-controller","system:discovery","system:public-info-viewer","system:service-account-issuer-discovery"] "failed rules"=["kosmos-node-not-ready"] "gvk"={"group":"","version":"v1","kind":"Pod"} "gvr"={"group":"","version":"v1","resource":"pods"} "kind"="Pod" "name"="example-deployment-6cc4fd9bd7-sb7m7" "namespace"="default" "operation"="DELETE" "policy"="kosmos-node-not-ready" "resource"="default/Pod/example-deployment-6cc4fd9bd7-sb7m7" "resource.gvk"={"Group":"","Version":"v1","Kind":"Pod"} "roles"=null "uid"="251f1877-4f2c-40ec-9bca-8ceb7c9c845f" "user"={"username":"system:serviceaccount:kube-system:node-controller","uid":"5a13be66-71fd-40e3-9553-00eb0825fbb0","groups":["system:serviceaccounts","system:serviceaccounts:kube-system","system:authenticated"]}